Chili peppers are a familiar ingredient in everyday meals across many cultures, especially in Asian cuisine. Beyond adding a distinctive spicy flavor, chili peppers are rich in vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds that can offer multiple health benefits when consumed properly and in moderation.
So, what vitamins are found in chili peppers, how do chili peppers benefit health, and who should limit their intake? Let’s explore in detail below.
Nutritional Components of Chili Peppers
Despite their small size, chili peppers are nutritionally dense and contain a wide range of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Vitamin C
Chili peppers are an excellent source of vitamin C, often containing higher levels than many common fruits. Vitamin C plays a key role in:
-
Strengthening the immune system
-
Protecting cells from oxidative stress
-
Supporting wound healing
-
Enhancing iron absorption
Vitamin A (from beta-carotene)
Chili peppers contain beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A. This vitamin helps:
-
Maintain healthy vision
-
Protect skin and mucosal tissues
-
Support immune function
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 contributes to:
-
Energy and protein metabolism
-
Nervous system function
-
Red blood cell formation
-
Brain health maintenance
Vitamin K1
Vitamin K1 is essential for:
-
Normal blood clotting
-
Bone health
-
Calcium metabolism
Minerals
Chili peppers also provide several important minerals, including:
-
Potassium – helps regulate blood pressure
-
Copper – supports red blood cell production
-
Iron – essential for oxygen transport in the blood

Health Benefits of Chili Peppers
1. Supports Immune Health
Thanks to their high vitamin C and antioxidant content, chili peppers help enhance immune defenses and protect the body against common infections.
2. Supports Heart Health
Bioactive compounds in chili peppers may help:
-
Improve blood circulation
-
Reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol
-
Support healthy blood pressure when consumed in moderation
3. Boosts Metabolism
Capsaicin stimulates heat production in the body, increasing energy expenditure and supporting weight management when combined with a balanced diet and active lifestyle.
4. Aids Digestion
In moderate amounts, chili peppers can stimulate gastric juices and support digestion. However, excessive intake may irritate the digestive tract.
5. Helps Regulate Blood Sugar
Some studies suggest capsaicin may improve insulin sensitivity and help stabilize blood sugar levels when chili peppers are consumed appropriately.
6. Pain Relief and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Capsaicin can reduce pain perception by interacting with nerve receptors and is widely used in topical treatments for muscle and joint discomfort.
7. Supports Skin Health
The combination of vitamins A and C in chili peppers helps:
-
Combat oxidative stress
-
Support collagen production
-
Promote healthier, more resilient skin
8. Benefits During Pregnancy (in Moderation)
Chili peppers provide folate (vitamin B9), which plays an important role in blood formation and helps reduce the risk of neural tube defects when consumed in suitable amounts.

Who Should Limit Chili Pepper Consumption?
Although chili peppers offer many benefits, some individuals should consume them with caution, including:
-
People with gastric ulcers or duodenal ulcers
-
Individuals with hemorrhoids or internal heat symptoms
-
Those with sensitive digestive systems
-
People experiencing mouth ulcers or eye inflammation
For these groups, chili peppers may worsen existing symptoms.
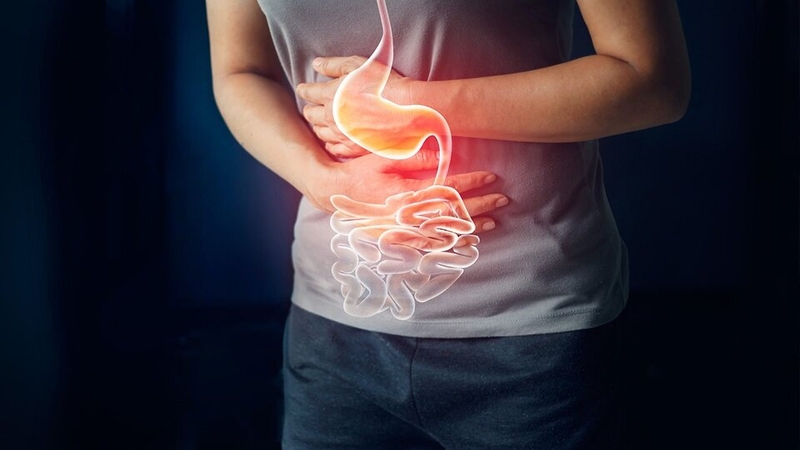
How to Consume Chili Peppers Safely
To enjoy the benefits of chili peppers without adverse effects, consider the following:
-
Consume chili peppers in moderation
-
Combine them with other foods during meals
-
Avoid eating chili peppers on an empty stomach
-
Drink enough water and include fiber-rich vegetables for balance
Chili peppers are more than just a spicy seasoning—they are a nutrient-rich food containing vitamins, minerals, and powerful bioactive compounds. When consumed properly, chili peppers can support immune function, digestion, metabolic health, cardiovascular health, and skin vitality. However, intake should always be adjusted based on individual tolerance and health conditions to avoid unwanted side effects.