Tomatoes are one of the most common and familiar foods in everyday meals. From simple home cooking to more elaborate recipes, tomatoes play an important role thanks to their distinctive flavor and versatility in combining with many other ingredients.
However, a common question often arises: Is a tomato a fruit or a vegetable?
This confusion comes from the fact that tomatoes share characteristics of both fruits and vegetables. In reality, to answer this question accurately, tomatoes need to be examined from two different perspectives: scientific classification and everyday culinary use.
The Difference Between Fruits and Vegetables
From a botanical perspective, fruits and vegetables are classified based on their origin and how they develop on the plant, rather than on taste or cooking methods.
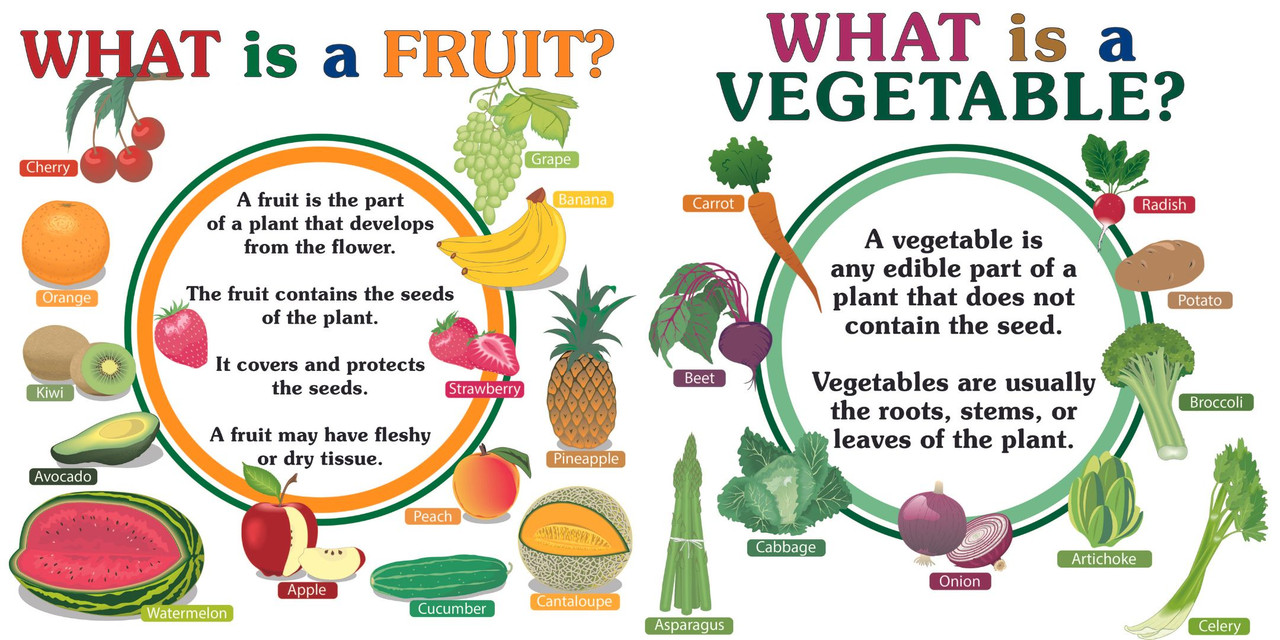
Fruits are parts of a plant that develop from the flower after pollination and typically contain seeds. Their biological role is to protect and help disperse seeds so the plant can reproduce.
Vegetables, on the other hand, usually refer to other edible parts of the plant such as leaves, stems, roots, or tubers. These parts do not develop from flowers and do not contain seeds.
In everyday life and culinary practice, however, fruits and vegetables are often categorized differently. Generally:
-
Foods with a sweet taste and often eaten raw or as desserts are considered fruits
-
Foods with a mild or savory flavor and commonly used in cooked dishes are considered vegetables
This difference between scientific definitions and culinary habits is the main reason tomatoes are frequently misunderstood.
Tomatoes Are Fruits
According to botanical classification, tomatoes are considered fruits, more specifically a type of berry. This classification is based on how tomatoes develop.
Tomatoes grow from the flower of the tomato plant after pollination. As the flower develops, the ovary enlarges and forms the fruit, which contains multiple seeds. These are defining characteristics of fruits in botanical terms.
Therefore, even though tomatoes are not particularly sweet like many common fruits, they fully meet the scientific criteria of a fruit. Similarly, foods such as cucumbers and eggplants are also botanically classified as fruits, despite being commonly treated as vegetables in cooking.

Why Tomatoes Are Commonly Used as Vegetables
Although tomatoes are fruits from a scientific standpoint, they are most often used as vegetables in everyday cooking. This is largely due to their flavor profile and culinary applications.
Tomatoes have a mild, slightly tangy taste rather than a sweet one, which makes them unsuitable for desserts. Instead, they are widely used in savory dishes such as soups, salads, sauces, and stews. In this context, tomatoes function much like other vegetables.
Additionally, in grocery stores and home kitchens, tomatoes are usually grouped with vegetables for convenience and practicality. As a result, in daily life and culinary traditions, tomatoes are commonly regarded as vegetables despite their botanical classification.

Tomato Powder – A Convenient Form of Tomato
In addition to fresh tomatoes, tomatoes are now also available in more convenient processed forms, one of which is tomato powder. Tomato powder is produced by drying tomatoes and grinding them into a fine powder, helping retain their characteristic color and tomato flavor.
Thanks to its dry, powdered form, tomato powder offers several practical advantages:
-
Easier storage compared to fresh tomatoes
-
Simple portion control when used in cooking
-
Suitable as a natural seasoning, for mixing into recipes, or for food preparation
Tomato powder is commonly used in dishes that require tomato flavor without the need for fresh tomatoes, making it especially suitable for modern lifestyles and long-term storage needs.
In summary, tomatoes are fruits from a scientific perspective because they develop from flowers and contain seeds. However, in everyday life and culinary use, tomatoes are commonly treated as vegetables due to their taste and how they are prepared in meals.